Polyethylene Terephthalate, commonly known as PET or PETE, is one of the most widely used polymers in the world. Known for its strong, durable, and lightweight properties, it has found extensive applications across various industries. But what exactly is PET, and why is it so important? In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the unique characteristics that make PET a standout polymer, its numerous applications, and the vital role recycling of PET plays in sustainable development.
PET was first synthesized in the mid-20th century and has since grown to be a cornerstone in the packaging industry due to its transparency and strength. Over the years, it has evolved from being primarily used in packaging materials to finding applications in textiles and even in the automotive industry. As the drive towards sustainability strengthens, the emphasis on recycling PET has become more significant than ever. Not only does recycling help conserve resources, but it also addresses mounting environmental concerns.
This article will delve into the various aspects of PET, starting from its origin, molecular structure, and properties, to its wide range of applications. We’ll also discuss the environmental impact of PET and the advances in recycling technologies that are helping to mitigate these effects. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll have a thorough understanding of this versatile polymer and its crucial role in modern society.
Properties of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
The success of PET in many industries can be attributed to its remarkable properties. As a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family, PET is characterized by its excellent mechanical strength, high clarity, and barrier properties that prevent the permeation of gases and liquids. These features make it particularly suitable for packaging applications, where maintaining the integrity and freshness of the product is paramount.
Additionally, PET is semi-rigid, which means it provides a balance between rigidity and flexibility. This is essential for containers needing to maintain their shape while being resilient enough to handle physical stress. PET also has a strong resistance to various chemicals, which further extends its usability in diverse environments and applications.
From a thermal standpoint, PET exhibits good thermal stability, which enables it to withstand various temperature ranges without degrading. This is especially useful in food packaging, where products might undergo refrigeration or slight heating.
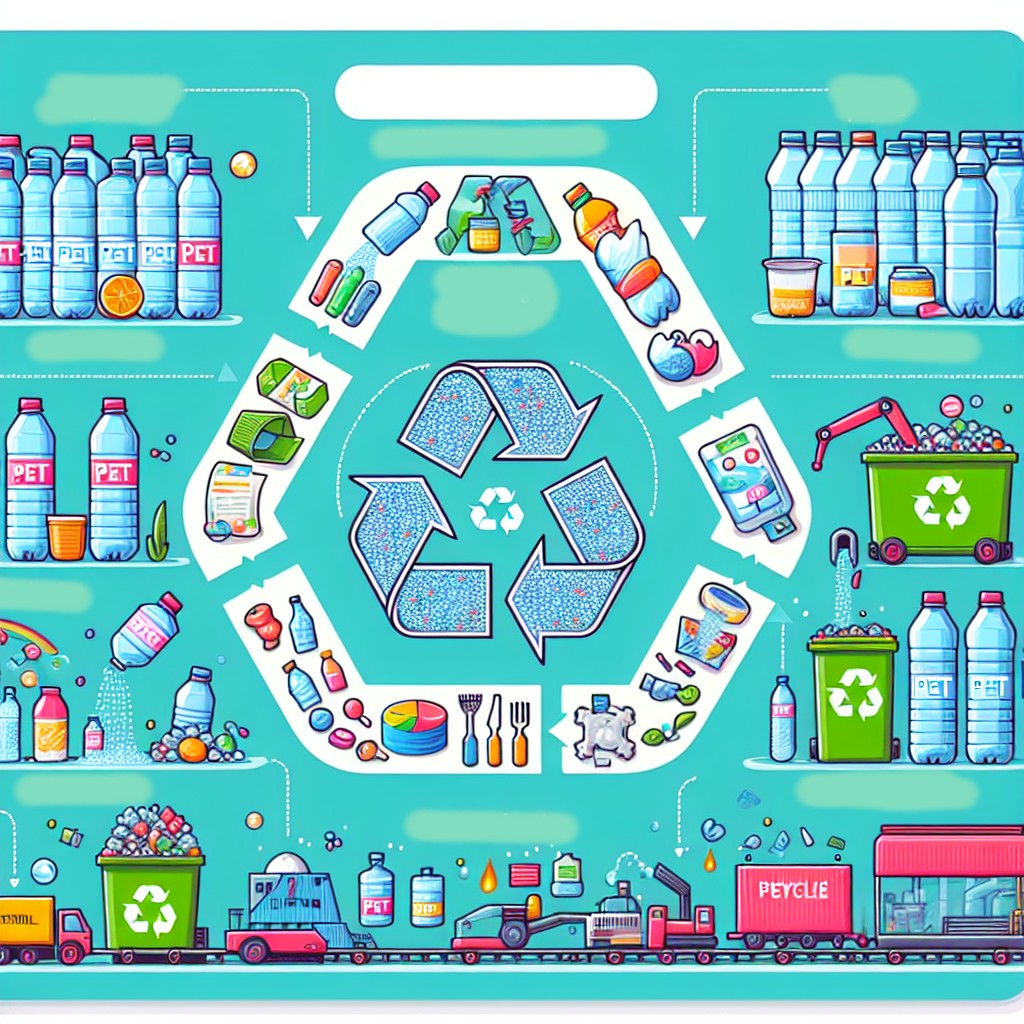
One of the most important aspects of PET is its recyclability. Unlike some other plastics that deteriorate after recycling, PET can be broken down and reformed multiple times without significant loss of quality. This property underscores its environmental significance and the efforts towards sustainable practices in the polymer industry.
Applications of PET
PET’s unique properties have enabled its extensive use across multiple sectors. One of the most well-known applications of PET is in the packaging industry. PET bottles for beverages like water and soft drinks are ubiquitous, owing to PET’s light weight and shatter-resistant nature. Furthermore, PET’s excellent barrier properties ensure that the contents remain fresh and uncontaminated.
Beyond beverage containers, PET is also used for packaging a variety of food products. PET trays, clamshells, and pouches are common in supermarkets, providing transparent and robust solutions for both fresh and processed foods.
In the textile industry, PET is often referred to as polyester and is widely used to make synthetic fibers. Clothes, home furnishings like curtains and bed linens, and industrial fabrics such as conveyor belts and safety belts often comprise this versatile polymer. Its strength, durability, and resistance to shrinkage and wrinkles make it a popular choice.
Additionally, PET has applications in the manufacturing of technical components in the automotive and electronics industries. Its use in automotive parts, such as bumpers, brings the benefits of reduced weight and improved fuel efficiency. In electronics, PET finds applications in insulating materials and flexible circuit boards.

Environmental Impact of PET
While PET has numerous benefits, its widespread use also brings environmental challenges. Single-use PET products contribute significantly to plastic pollution, particularly in marine ecosystems. Mismanagement of PET waste can lead to severe ecological consequences, affecting wildlife and human health.
However, the recyclability of PET offers a pathway to mitigate these environmental impacts. PET is one of the few plastics that can be 100% recycled, which means that every PET bottle or container could potentially be reborn into a new product.
The environmental footprint of PET can be reduced through effective recycling systems and consumer awareness. By promoting recycling, we can ensure that PET waste is managed responsibly and doesn’t end up in landfills or oceans.
Additionally, innovations in PET production processes aim to reduce the environmental impact right from the manufacturing stage. Advances in polymer chemistry are enabling the creation of PET with lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions.
Advances in PET Recycling Technologies
Recycling PET is not just about reducing waste; it is also about creating a sustainable cycle of reuse. Traditional recycling methods involve melting down PET and reforming it into new products, but this can sometimes degrade the material properties. Recent technological advancements are addressing these limitations.
One such innovation is chemical recycling, which breaks down PET into its base monomers. These monomers can then be purified and repolymerized into PET with properties comparable to virgin material. This method allows for endless recycling without a loss in quality, thereby supporting a closed-loop recycling system.
Another promising development is the use of enzyme-based recycling. Certain enzymes can degrade PET into its precursor chemicals under mild conditions. This biological approach offers a potentially more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional recycling methods.
Governments and organizations worldwide are also investing in improving collection and sorting processes to ensure that PET waste is efficiently recycled. Initiatives like deposit-return schemes and increased public awareness campaigns are crucial in driving up recycling rates and reducing plastic waste.
Economic Impact of PET
Beyond environmental considerations, the PET industry also has significant economic implications. The production, application, and recycling of PET generate employment opportunities and contribute to the global economy. The packaging industry, in particular, relies heavily on PET due to its cost-effectiveness and performance attributes.
In regions where recycling infrastructure is well-developed, the PET recycling industry can be highly lucrative. Reprocessed PET, known as rPET, is in demand, especially as companies strive to meet sustainability goals and consumer preferences for environmentally friendly products.
Investments in recycling facilities and technology also fuel economic growth by creating jobs and fostering innovation. Additionally, the use of rPET lowers the dependence on fossil fuels, which can result in cost savings and reduced volatility in raw material prices.
However, the global PET market is influenced by various factors, including crude oil prices, regulatory policies, and consumer trends towards sustainability. As the industry adapts to these dynamics, it continues to evolve, driving both economic and environmental benefits.
Conclusion
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is undeniably a pivotal material in modern manufacturing and packaging. Its unique properties such as strength, clarity, and resistance to chemicals have made it indispensable across various applications, from beverage containers to automotive components. However, the extensive use of PET also underscores the importance of sustainable practices, particularly recycling.
With advancements in recycling technologies, PET’s life cycle can be extended, contributing to resource conservation and reducing environmental pollution. Chemical and enzyme-based recycling methods hold promise for maintaining the material’s quality while supporting a circular economy.
The economic impact of PET is significant, providing job opportunities and supporting industries worldwide. As the focus on sustainability grows, the demand for recycled PET is likely to increase, driving further innovations and investments in recycling infrastructure.
Ultimately, the future of PET lies in balancing its widespread utility with responsible environmental practices. Through improved recycling efforts and sustainable manufacturing processes, we can harness the benefits of PET while minimizing its ecological footprint. By doing so, we contribute to a more sustainable and economically viable world.